RIYADH: Saudi Arabia has established itself as a global leader in the rapidly advancing water desalination market, doubling its production capacity, while developing new technology to repurpose the harmful byproduct of the process — brine.
While desalination is effective for achieving water sustainability, producing drinking water from sea water in arid regions, it leaves behind a highly concentrated saline fluid. If this brine is disposed of back into the sea without treatment, it poses a potential danger to marine ecosystems.
Simply put, brine is highly concentrated seawater that contains contaminants, including chemicals used during the desalination process.

“The chemicals should be all neutralized,” said Noreddine Ghaffour, a research professor at the Water Desalination and Reuse Center at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST).
He told Arab News that “there is no reason to dump chemicals into the sea, because they are all negatively affecting marine life, including chlorine and antiscalants.”

KAUST Professor Noreddine Ghaffour. (Supplied)
Water desalination scientists in Saudi Arabia have developed technologies to neutralize chemicals in brine before discharge and to disperse salt over a radius of up to 2 km when reintroduced into the sea.
Ghaffour, who was granted Saudi citizenship for his work and expertise on desalination, said that researchers and industry experts believe the future of the process is in recovering minerals, while treating the brine and achieving zero liquid discharge.
While around 70 percent of Earth is covered in water, only 2.5 percent of it is fresh, of which 1 percent is easily accessible, according to the National Geographic website.

Water desalination separates salt ions from sea water to make it safe for consumption. Salinity levels vary by body of water; for example, the Red Sea has 40 grams of salt per liter, while the Arabian Gulf’s salinity is 45 grams per liter.
The main water desalination technologies employed globally are: reverse osmosis, which separates salt ions from water molecules through a semipermeable membrane; multi-stage flash and multi-effect distillation, which are thermal processes that use evaporation and condensation; and electrodialysis, where electricity drives the salt ions in the water towards electrodes to be removed.
All three technologies produce brine, but reverse osmosis plants generate lower quantities compared with the other two methods.
DID YOUKNOW?
• Some elements, like lithium, are 5,000 times more abundant in the ocean than on land. Lithium is crucial for Li-ion batteries. (Source: KAUST)
• In 2021, Saudi Arabia set a world record for the lowest energy consumption in mobile desalination, reducing it to 2.27 kWh/m³. (Source: Desalination Lab)
• By 2040, 33 countries, including 14 in the Middle East, are projected to face extreme water stress. (Source: Desalination Lab)
Reverse osmosis, according to Ghaffour, uses a method called membrane separation, where osmotic pressure is overcome by a semipermeable membrane that filters out salt ions, allowing only water molecules to pass through.
Ghaffour explained that semipermeable membranes filter out the salt and reject it into the brine. The high rejection rate, which is about 99 percent, leads to the production of highly saline brine.
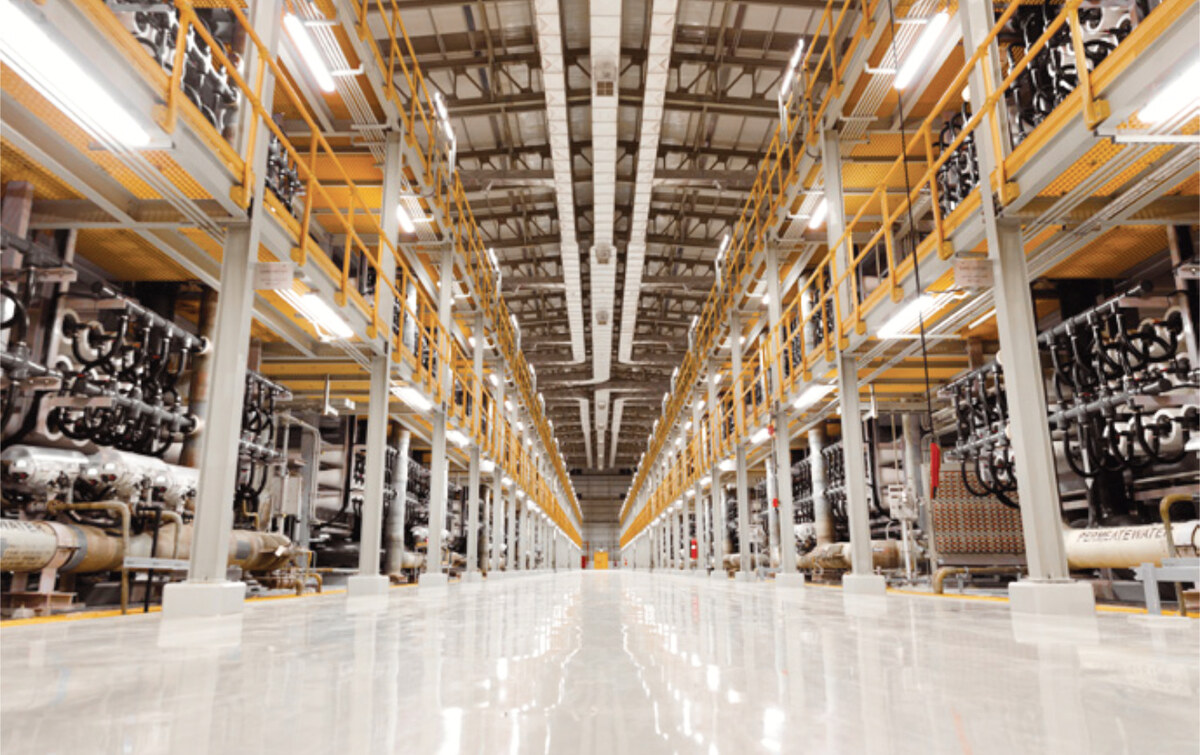

After pretreatment, the feed water is introduced to the RO system, where dissolved solids are removed, and freshwater is produced. (Photo courtesy: Saudi Water Authority)
Moreover, osmotic pressure — the force applied to a solution to prevent a solvent from passing through a semipermeable membrane — requires a lot of electrical energy.
“Electricity is one of the most expensive energy forms… the main problem with (reverse osmosis) is that we do this under pressure,” the KAUST professor said.
He added: “The more salt, the higher the osmotic pressure. In order to pass only water molecules through the membrane, we need to apply a pressure which is higher than the osmotic pressure.
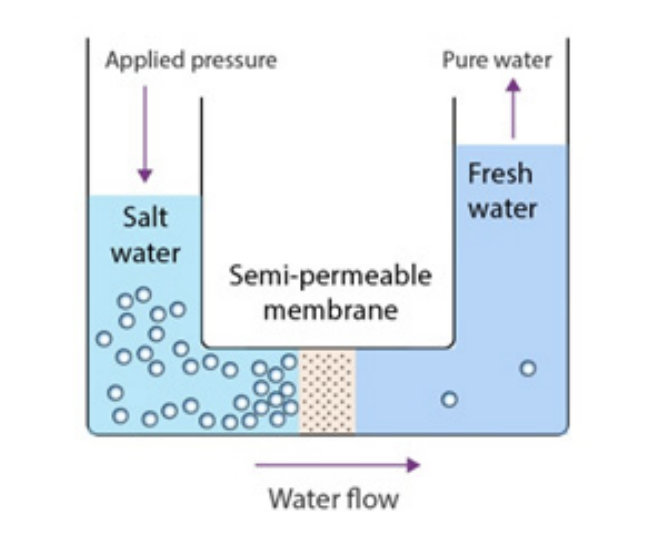
Illustration courtesy of the Saudi Water Authority
“And the osmotic pressure in Red Sea water, for instance, is 30 bar… so we need a pressure higher than 30 bar, which is a very high pressure.”
He also explained that “recovery” refers to “how much water we recover from the sea,” adding that “if the recovery is 50 percent, this means that salt contents are doubled.”
Ghaffour said selecting the correct location for a desalination plant is highly important. Authorities must choose sites with a reliable water intake that will not disrupt marine ecosystems or impact densely populated areas.
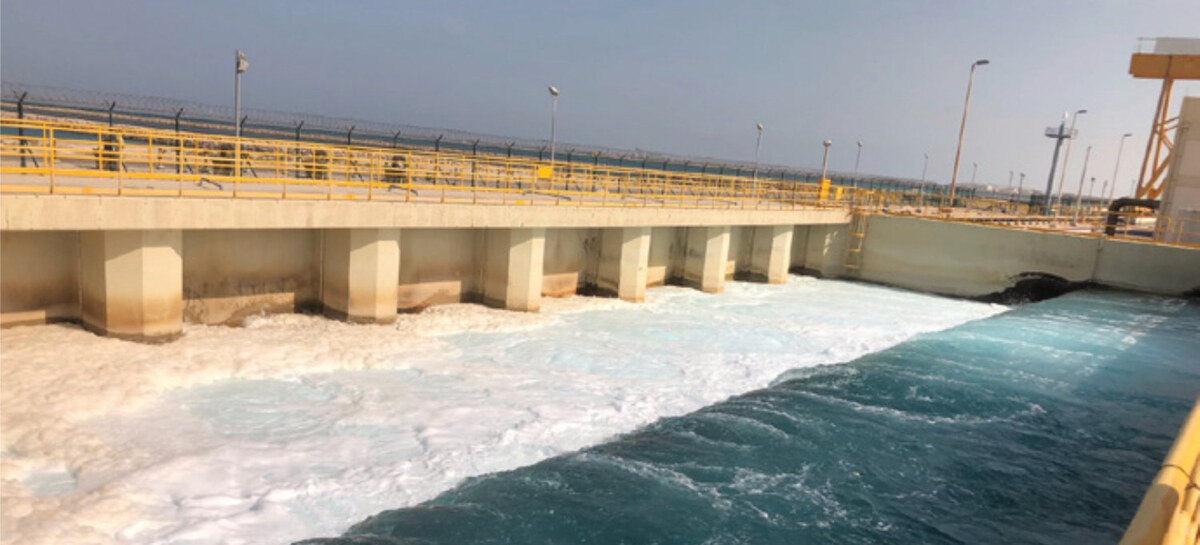

A view of an outfall system of desalination plant, which handles the safe discharge of treated wastewater back into the environment. (Photo courtesy: Saudi Water Authority)
According to the UN Environment Programme, unless waste water is properly treated and dispersed, it may form a dense plume of toxic brine, which can degrade coastal and marine ecosystems.
Increased salinity and temperature can reduce dissolved oxygen levels and contribute to the formation of “dead zones” — areas where few marine species can survive.
Ghaffour said that while brine is bad for the environment, it has not caused significant global environmental harm. Over the past 30 to 40 years, Saudi Arabia and the Gulf region have experienced few negative side-effects from the desalination process, he said.
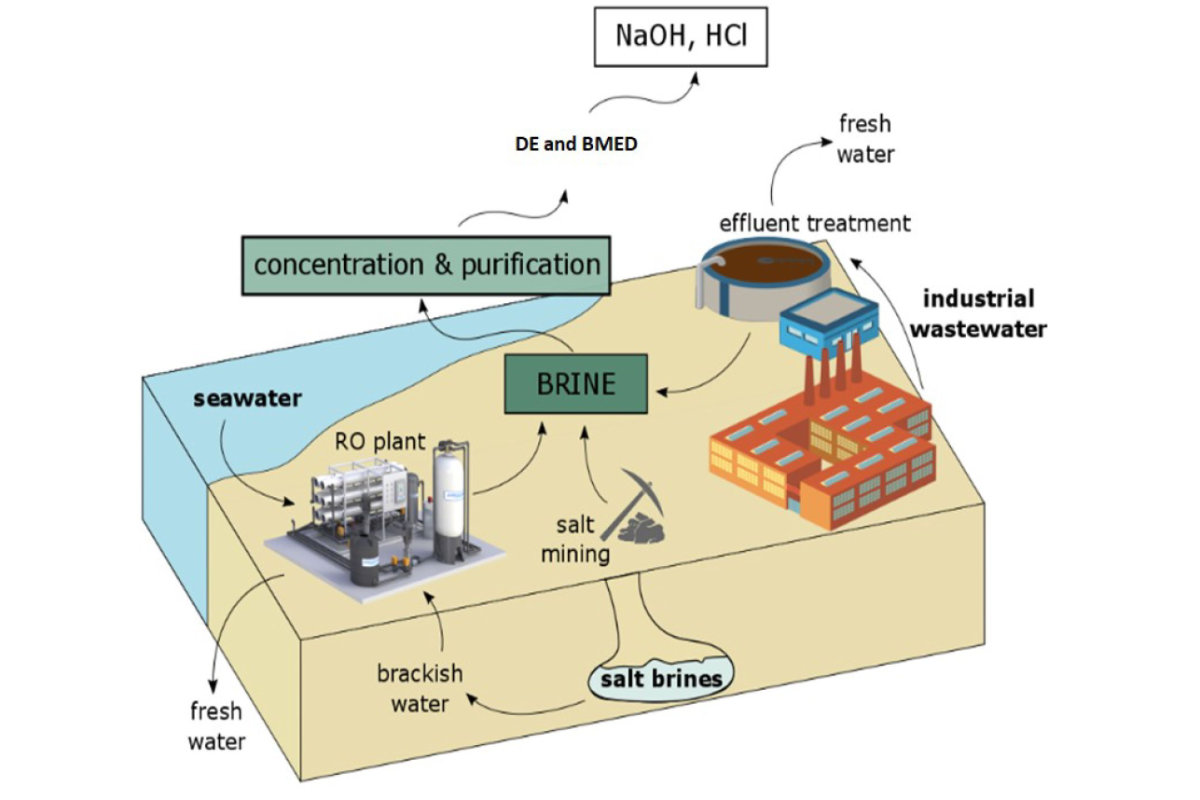
Processing brine to yield useful chemicals such as NaOH and HCl. (Infographic courtesy of MIT News)
Concern over waste water from desalination returning to the sea at a higher temperature is less of an issue with the reverse osmosis method, Ghaffour said. “We have the same temperature as sea water, maybe one degree more, which is affordable.”
Researchers are determined to achieve zero liquid discharge, which involves treating brine until only solids remain. However, this process also concentrates all the salts in the same place.
To remove salt ions from brine, a complex and costly process called mineral recovery is used.

Brine from water desalination as a raw material. (Courtesy of global-recyling.info)
The challenge in mineral recovery lies in the fact that high-value minerals, such as lithium, rubidium, and uranium, are present in brine at very low concentrations.
To make the process efficient and economically viable, further technological advancements are needed.
Currently, “there are no technologies to handle this huge volume,” Ghaffour said. “We are talking about huge volumes of water, like 1 million tons of water (recovered) every day, it’s higher than a river.”
Several technologies have been developed for mineral recovery on a smaller scale. One method involves chemical treatments that precipitate different salts in stages, starting with calcium carbonate and ending with lithium.
Another mineral recovery method involves the use of ion exchange membranes or absorbents designed to capture specific minerals, such as lithium.
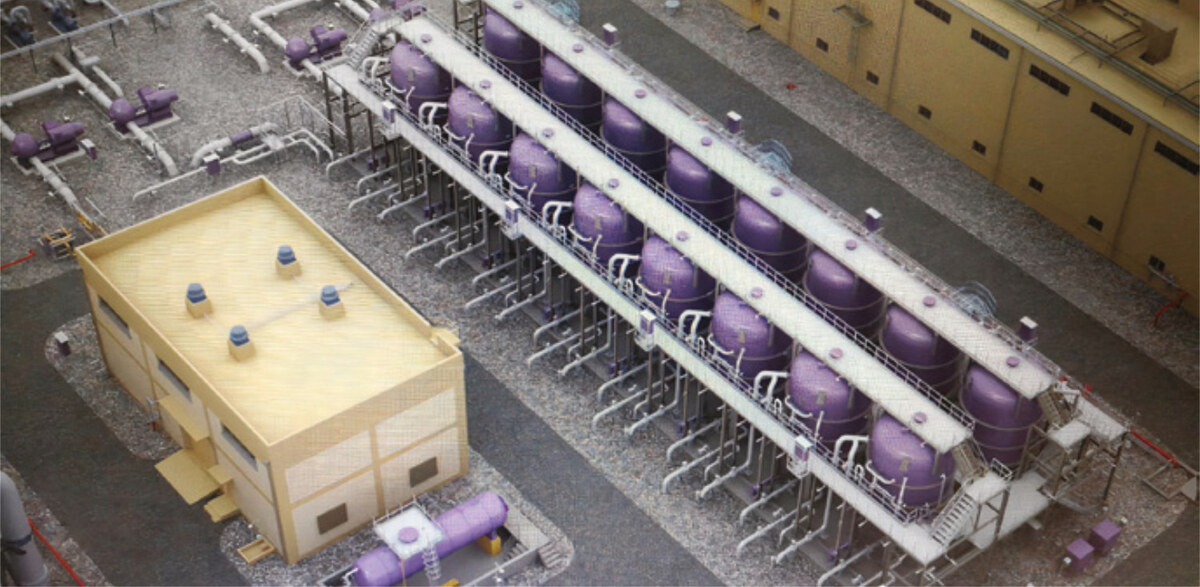

The post-treatment stage process is mainly for stabilization, corrosion control, disinfection, and air stripping for CO2 & H2S removal. (Photo courtesy: Saudi Water Authority)
One of the largest areas of current research is the magnesium hydroxide family, particularly for its applications in the cement and concrete industry.
Saudi Arabia is already using nanofiltration technology to produce magnesium from magnesium-rich waters, with the next step being the extraction of magnesium hydroxide for cement production.
Expensive and critical minerals like rubidium — which costs around $3,000 per kilo — as well as uranium and lithium, are of great interest, but are costly to extract due to their low concentrations, requiring significantly more energy in the process.
From a commercial perspective, businesses prefer to purchase lithium from produced water — a byproduct of oil and gas production — rather than from brine.
Brine can also be repurposed to enhance the efficiency of the desalination process. Due to its high osmotic potential, brine can be used for energy production.
Ghaffour said that several companies are utilizing reverse electrodialysis to generate energy, which is then used to power the reverse osmosis process.
In addition, to achieve a circular carbon economy, reverse electrodialysis can be combined with brine dilution for mineral recovery, allowing part of the brine to be reused in an efficient closed-loop system.
“This is what I call a seawater factory,” Ghaffour said. “We take seawater and we produce everything from seawater without polluting back.
“Many experts are saying that in the future, desalinated water, which is what we need most, will itself be a byproduct, because we will have so many more valuable products from the sea. Then this desalinated water will be just one of the byproducts.”
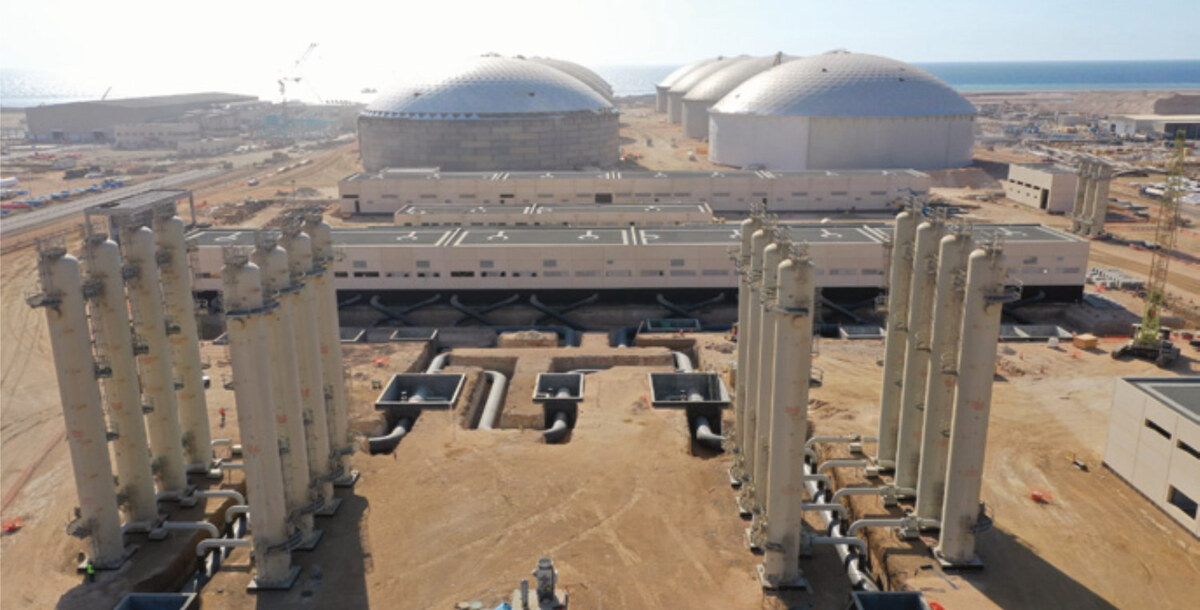

Operational tanks are used to store freshwater for distribution through transmission lines. (Photo courtesy: Saudi Water Authority)
However, he believes that turning this vision into reality will take time.
“We have to distinguish between two things. One is science and the second one is technology scale-up.”
In September 2024, Lihytech, a KAUST startup, announced a partnership with Aramco to strategically collaborate on recovering lithium from oilfield brines using direct lithium extraction technology and a membrane developed at KAUST.
Ghaffour is also collaborating with a Singaporean company, MediSun Energy, to integrate desalination with energy and mineral production, aiming to optimize these processes as a whole. A pilot facility has already been installed in South Korea, with plans for another installation in Saudi Arabia.
“The whole world is working on this (mineral recovery and optimizing desalination). We will see a lot of developments in this, in my opinion,” he said.

































